Regularmente cuando las personas quieren ampliar o redecorar su jardín, se enfrentan al problema del trasplante de los brotes desde la maceta a la tierra en la que se desea hacer el cultivo. Esta situación resulta complicada por dos motivos, primero muchos expertos indican que el trasplante puede ser nocivo para el cultivo, ya que puede maltratar y romper sus raíces las cuales ya tal vez no vuelvan a crecer una vez en la tierra y el segundo, las macetas actuales generan altos costos económicos y ambientales. El proyecto busca fabricar macetas a partir de sargazo, destinadas a diferentes tipos de cultivos (horticultura, viveros de plantas ornamentales, de temporada, forestales, etc.), sin afectar a los mismos y a las tierras en el que se vayan a sembrar para su crecimiento. Estas macetas son prácticas, útiles y degradables. Evitan el shock que produce la trasplantación porque esta se puede hacer sin necesidad de sacar las plantas del sustrato, no es difícil que se degraden en un tiempo corto que beneficiará a la planta, aporta nutrientes que las plantas necesitan para sobrevivir; y las raíces no tendrán ningún problema para seguir creciendo después de traspasar las paredes de la maceta, para llegar a la tierra.
Se deben buscar alternativas de uso para el sargazo ya que su arribo masivo esta ocasionando problemas ambientales, por otro lado las personas enfrentan el problema del trasvasije de los brotes o árboles desde el macetero a la tierra ya el trasplante puede ser nocivo para las plantas, y por otro lado, a muchos les complica cortar la maceta sin destruir las raíces. Las macetas impermeables a las raíces producen deformaciones en ellas y las macetas de plástico que proliferan últimamente así como la bolsa de plástico para cultivo resultan ser un grave problema de contaminación para el medio ambiente.
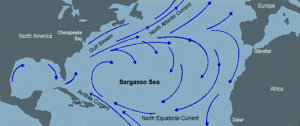
El sargazo pelágico es un alga parda, o alga que flota libremente en el océano y nunca se adhiere al fondo del océano provee refugio para especies migratorias y hábitat esencial para más de 120 especies de peces y más de 120 especies de invertebrados El sargazo circula constantemente entre el Mar de los Sargazos (en el océano Atlántico), el Caribe, el Golfo de México y la corriente del Golfo.

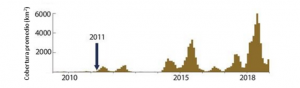
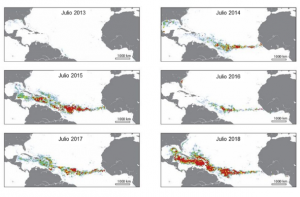
Al ser un organismo flotante, el sargazo se mueve a través del océano arrastrado por el viento y las corrientes marinas y ocasionalmente arriba de forma natural a las costas. Sin embargo, desde 2011 se ha observado un crecimiento masivo y sostenido de estas especies en el Atlántico, hasta alcanzar una longitud de 8,850 kilómetros en 2018 (aproximadamente la distancia que existe entre la CDMX y la Patagonia), formando al que se ha llamado el “Gran Cinturón de Sargazo” con una biomasa aproximada de 20 millones de toneladas; cifra equivalente a 10 veces el total de la pesca y la maricultura anual nacional.
El origen de este fenómeno sin precedentes está vinculado con cambios en los vientos y la hidrodinámica de las corrientes originados por el cambio climático que podrían estar trayendo el sargazo desde el oriente (África) transportado por las corrientes zonales, o venir costeando desde el sur del continente americano (Brasil), o proceder del Mar de los Sargazos.
Aumento en las descargas de materia orgánica y nutrientes (Río Amazonas) que favorece el crecimiento de las algas Sargassum las cuales duplican su tasa de crecimiento en menos de 18 días.
Aumento en la temperatura superficial de los océanos que favorece el desprendimiento del sargazo de su sustrato.

Ha tenido un impacto negativo muy importante porque si el sargazo continúa llegando en el volumen registrado en 2015 y 2018 y no se le da un manejo adecuado se puede colapsar la industria turística de Quintana Roo causando pérdidas económicas por cancelaciones, pérdida de empleos por la disminución de turismo, afectación de la economía local (prestadores de servicios de las comunidades), además del aumento en los costos de manejo y limpieza de playas en los hoteles.
El aspecto negativo del paisaje en las playas y zona costera en general, provoca bajas en el turismo.
Incremento de los gastos para la limpieza de playas. El volumen de sargazo que llegó durante el 2019 superó la capacidad de los hoteles para removerlo.
Se ha demostrado que el sargazo produce reducción de luz y oxígeno (hipoxia y anoxia), aumento en las concentraciones de nitrógeno y fósforo (eutroficación), contaminación de los suelos y el oceáno por la generación de ácido sulfhidrico (H2S) y amoniaco (NH3) , ademas del mal olor que esto ocasiona.
Las reservas ecológicas de Sian Khan, Puerto Morelos, Akumal, estan siendo afectadas, la mortandad de los arrecifes de coral, Interferencia con la anidación y eclosión de tortugas, Mortalidad de los pastos marinos cercanos a la costa, Mortalidad de diversos animales marinos, Impacto en especies de fauna asociadas al sargazo durante las actividades de remoción en el mar
Acumulación masiva en la playa (con algunos animales muertos), Pérdida de playa como consecuencia de la desaparición de praderas de pastos marinos y por actividades de remoción en tierra.
Interrupción en las actividades pesqueras en la costa y en las comunidades
Pérdidas económicas de los pescadores por mortandad de los recursos pesqueros
Malestar de lancheros ya que sus maquinarias (lanchas) se atascan y estropean con el sargazo
La mala disposición del sargazo que se recoge en las playas puede contaminar el acuífero y afectar la disponibilidad de agua a las comunidades costeras y contaminar el mar.
La descomposición del sargazo puede provocar daños en la salud, por respirar los gases del sargazo derivados de la acumulación del mismo (H2S y NH3) .
Genera condiciones para la crianza de moscos como vectores de enfermedades para el ser humano.
Ocurren problemas de salud en los bañistas y prestadores de servicios acuático por contacto con el sargazo (y la fauna que lo acompaña).
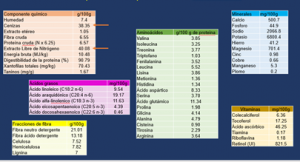
Iodo
Fucoxantina – pigmento con actividad antioxidante
Compuestos fenólicos – actividad antioxidante
Ácido alginico y Fucoidano – polisacaridos hepatoprotector, actividad anticoagulante, antiviral, antibacteriana, antitrombótica, antioxidante, inmunomoduladora, antiinflamatoria, prebiótica, protegen mucosa gástrica contra la actividad proteolítica de los jugos gástricos, previenen la infección en el estomago por Helicobacter pylori.
Se han hecho diversos estudios y pruebas para aprovechar el sargazo las cuales han tenido excelentes resultados; se ha utilizado para alimento de animales, construyen casa con ladrillos de sargazo
el invento portomorelense se utilizaría en viviendas para personas de escasos recursos en quintana roo y ayudaría a enfrentar el problema del recale masivo de algas, materiales para acabados, como ladrillos y tablas similares a la madera, que pueden ser una opción decorativa para el hogar, una empresa diseñada por un grupo de jóvenes mexicanos se fundó en Cancún Quintana Roo, creando la primera planta piloto para procesar sargazo en México y obtener alginato de sodio; investigadores han podido obtener celulosa que se podría usar en más de 20 tipos de industrias, sargazo como sustrato para hongos y bioplastico de sargazo son los usos que se le ha dado a esta alga.
Se han propuesto los siguientes usos:
En el trasplante se produce contacto con el aire esto detiene su crecimiento y estimula la formación de raíces secundarias que ocupan todo el volumen de la maceta.
El espacio de la maceta es muy pequeño por lo que las raíces no pueden extenderse para buscar agua y nutrientes, por lo que hay que prestar más atención tanto al riego como al abonado. Y muchos de los substratos para macetas, en general, son pobres en elementos fertilizantes y el agua sobrante del riego que sale por el agujero de drenaje va arrastrando nutrientes, empobreciéndolo poco a poco. Las macetas de plástico biodegradables, no ayudan en nada al medio ambiente, porque tardan mucho tiempo en descomponerse.
Por orto lado el zargazo contiene minerales que aceleran al crecimiento de las plantas y es 100% biodegradable, ya que en estos momentos se estan prohibiendo el uso de plasticos esta es una excelente opción tanto en casa como a nivel productor.
De acuerdo con los materiales utilizados, la cantidad de variantes en macetas biodegradables pueden clasificarse en dos grandes grupos:
Los materiales utilizados en las macetas fabricadas con fibras vegetales son papel, fibra de madera, fibra de coco, yute, turba y Miscanthus, Algunos de estos tipos ya se encuentran desde hace varios años para aplicaciones especiales, Los viveros han tenido muy buenas experiencias utilizando macetas de papel para presentar plantas cubresuelos para importantes clientes del sector servicios.
Materiales fósiles, renovables, o mezclas de ambos constituyen la base de los materiales biodegradables, estos materiales deben estar hechos mayoritariamente de materiales renovables de origen vegetal.
En particular, los materiales más utilizados para fabricar macetas biodegradables son la turba, las virutas de madera, fibra de coco y papel reciclado. Con los materiales fibrosos, el crecimiento de las plantas es con frecuencia mejor durante el cultivo, y la colonización del suelo por las raíces después de la plantación es más rápida.
Existen en el mercado diferentes tipos de macetas biodegradables principalmente hechas con carton y fibras naturales pero con el agua y la humedad este material se pudre y tiende a ser un excelente nido para los hongos, lo que puede ser perjudicial para la salud de las raíces de las plantas.
Cuando las personas quieren ampliar o redecorar su jardín con nuevas plantaciones, se enfrentan al incómodo problema del trasvasije de los brotes o árboles desde el macetero a la tierra. Esta situación es una complicación por dos motivos: primero, muchos expertos indican que el transplante puede ser nocivo para las plantas, y por otro lado, a muchos les complica cortar la maceta sin destruir las raíces.
En síntesis, en esta acción las raíces de la planta corren peligro y para quien ama sus jardines o hace de esta labor un oficio, es una necesidad dar con una alternativa más segura. Es aquí donde las macetas biodegradables se plantean como la solución ecológica a una necesidad con una importante demanda.
Estas macetas son prácticas y útiles para las plantas. Sirven para evitar el shock del transplante porque puedes transplantar sin necesidad de sacar la planta del sustrato, las macetas son biodegradables y las raíces pueden atravesarlas sin problemas.
Esta diferencia es muy notable, especialmente en condiciones difíciles (frío, sequía, estaciones desfavorables…). Por último, la no deformación del sistema radicular asegura una buena y rápida fijación de la planta y una mejor exploración del suelo.
En México ya existe una empresa que se unió a esta tendencia ecológica: Sedano, vivero ubicado en Guadalajara, a través de la línea denominada Ecopot. Su línea de macetas, consiste en macetas biodegradables perfectas para el hogar y jardín, que pueden ser usadas para plantas en crecimiento, y posteriormente pueden ser quebradas para permitir el crecimiento de las raíces y plantadas directamente en la tierra o usadas en el interior con las flores.
Las macetas Ecopot son hechas de fibra de bambú, cáscara de arroz y paja, con un método de alta presión combinado con altas temperaturas. Todas las macetas de esta línea no contienen madera o petróleo, son biodegradables y no dañan el medio ambiente.
Algunas empresas realizan macetas con fibra larga del Kenaf y tienen el tamaño necesario para acoger el volumen adecuado de tierra y de la composición de la enmienda que da mejores resultados con cada especie a usar.
Maple Vila, empresa de Uruguay que ofrece al mercado macetas biodegradables para viveros, compuestas de celulosa y fibra vegetal.
Ecoforms, empresa de California, EEUU ofrece son hechas de cáscaras de granos y agentes naturales. En ninguna etapa del proceso de producción se usan o producen agentes contaminantes.
CocoPot, empresa Alemana, realiza macetas biodegradables de fibra de coco y rizado, que está formada exclusivamente por el látex natural comprimido (leche árbol del caucho), un aglutinante para formar una unidad elástica y la naturaleza provee las materias primas en grandes cantidades.
Alecoconsult Internacional, empresa con presencia en África, América, Asia y Europa macetas fabricadas a base de fibras de origen vegetal. El proceso de la biodegradación empieza dependiendo de la temperatura ambiental, humedad relativa y presencia microbiana a partir del momento de la aplicación. La biodegradación completa depende del grosor del plástico.
Hay que tener en cuenta que las macetas de plástico convencionales a base de polietileno no se biodegradan y generan un alto nivel de residualidad.
La necesidad de disminuir la dependencia de productos químicos artificiales en los distintos cultivos, está obligando a la búsqueda de alternativas fiables y sostenibles. En la agricultura ecológica se le da gran importancia a este tipo de abonos y cada vez más se están utilizando en cultivos intensivos.
No podemos olvidar la importancia que tiene el mejorar algunas características físicas, químicas y biológicas del suelo y, en este sentido, este tipo de abonos juega un papel fundamental .
Con estos abonos, aumentamos la capacidad que posee el suelo de proveer a las plantas los distintos nutrientes que éstas necesitan.
A veces se presentan carencias de nutrientes. Consiste en que falta uno o varios de los 12 elementos esenciales para toda planta (Nitrógeno, Fósforo, Potasio, Magnesio, Calcio, Azufre, Hierro, Manganeso, Molibdeno, Zinc, Cobre y Boro), lo que ocasiona síntomas diversos.
El sargazo contiene:
Calcio, fosforo, sodio, potasio, hierro, manganesio, cobre y zinc en las cantidades esenciales que alimentan a las plantas y les ayuda a un mejor crecimiento.
Elaborar macetas a base de sargazo ya que es rico en nitrógeno que es un elemento primario de las plantas, para favorecerlas como fertilizante y que ademas puede servir como sustrato aportando minerales esenciales.
Nos interesa este tema porque en las playas del Caribe están arribando cantidades masivas de sargazo, debido al aumento en las descargas de materia orgánica y nutrientes que favorecen su crecimiento (es como si el mar te dijera te regreso toda la basura que me has dado), también esta afectando calentamiento global ya que el aumento en la temperatura superficial de los océanos lo cual favorece el desprendimiento del sargazo de su sustrato, finalmente el cambio en las corrientes marinas arrastra el sargazo a las playas.
Si logramos elaborar macetas a base de sargazo, entonces utilizaríamos un producto que es poco común, ya que posee propiedades que pueden ser favorables al desarrollo de la planta además de ser un producto económico y amigable con el medio ambiente.

Agua
Vinagre
Fécula de maíz
Sargazo seco
Aceite
Taza medidora
Cucharas medidoras
Pintura vegetal
Recipientes
Vasos para moldear las macetas
El sargazo se debe recolectar de mar adentro para estar seguros que esta vivo y no en proceso de descomposición.

Una vez recolectado se lava y se deja secar perfectamente al sol.


Se tritura para guardarlo envasado
Una vez que ya se tiene el sargazo seco y triturado está listo para usarse.

Poner la fecula de maíz en un recipiente junto con el agua y revolver hasta que no queden grumos

Poner en 200 ml la grenetina para hidratarla

Poner a fuego lento hasta que la mezcla cambie de color

Poner el colorante vegetal para darle color a la maceta

Poner el sargazo en abundante cantidad, apagar a la lumbre, poner el vinagre y comenzar a amasar

Poner la masa en moldes para darle forma y dejar secar unos días.


Antes de iniciar con el germinado se realizaron pruebas de permeabilidad al agua y de resistencia mecánica.


Llenar la maceta con agua y medir el tiempo que tarda en atravesar las paredes. Se observa como la maceta se humedece y se vacía muy rápidamente. (Por eso los recipientes no tienen agujeros en la base). La porosidad se ve a simple vista.
Se le aplico fuerza para deformar el recipiente no logrando deformarlo ni romperlo.


En las macetas pequeñas se colocó sargazo como sustrato para su germinado y semillas de chile serrano y chile habanero.

En las macetas mas grandes se utilizo tierra de jardín convencional y sargazo, se sembraron semillas de chile serrano, jalapeño.

Se utilizaron macetas biodegradables comerciales para comparar resultados.
Se deben regar para mantener el recipiente húmedo, pero sin exceso.
Ponerlas en un lugar con luz, pero no directo al sol.
Tomó 3 días en germinar en las macetas de sargazo.
Aquí se observa el crecimiento de las semillas en una semana. Se puede ver que las primeras hojas ya han salido.

La velocidad de germinación es muy diferente entre las macetas, se observa que en las macetas de sargazo crecieron más rápido y germinaron más semillas que en las macetas biodegradables comerciales y la de plástico solo germino una semilla mas lentamente que en las macetas anteriores.
Su resistencia es útil durante todo el ciclo del cultivo, no se rompe en el transporte y ofrece a la planta un contenedor estable.
Dejamos dos semanas así, cuando las pequeñas plantas tienen sus tallos largos se pasan a tierra ya que las macetas de sargazo comenzaban a degradarse y así el crecimiento de las raíces no se vió frenado por el contacto con el aire.
Esto le ayuda a la planta a mejorar la absorción de agua y nutrientes. La porosidad obliga a una ramificación más natural en la estructura de la raíz.
Se hizo un contenedor con vidrio para poder apreciar la degradación de las macetas.

Después de 15 días a tres semanas de haber pasado las macetas a tierra se obtuvieron los siguientes resultados:

Las macetas se degradaron más rápidamente que las macetas biodegradables comerciales y en la maceta de plástico, se observa que las plantas en estas macetas han crecido más rápidamente que las demás.

La permeabilidad, porosidad y resistencia de las macetas se consideran adecuadas.
Usando la maceta de sargazo como fertilizante a los 15 días de trasplante se observo que con el tratamiento del sargazo, las plantas crecieron mejor que aquellas que no tuvieron ningún tratamiento.
Comparando con plantas sembradas en macetas biodegradables comerciales se observa mejor desarrollo de las raíces en la maceta biodegradable a base de sargazo.
De acuerdo a la literatura la velocidad de degradación va es función de diferentes parámetros relacionados esencialmente con la vida microbiana del suelo, esto hace suponer que en poco tiempo y con clima templado, sólo deberán quedan pequeños trozos de pared al cabo de algunos meses.

Se continuará monitoreando el crecimiento de estas plantas.
(Da clic)

Es posible fabricar macetas biodegradables a base de sargazo que resultan ser un producto de bajo costo y apto para distintos tipos de cultivo. La planta germinada en la maceta biodegradable de sargazo no necesita trasplante: se puede introducir “maceta dentro de maceta” o “maceta en suelo”, sin dañar las raíces, lo que permite adelantar los ciclos de trasplante en propagación y evitar el shock de trasplante. Estos recipientes se plantean como una alternativa para quienes aman sus jardines o hace de esta labor un oficio y buscan productos “listos para plantar”. Es aquí donde los recipientes biodegradables se plantean como la solución ecológica que cubre una necesidad de forma más segura y con una importante demanda.
Al cultivar en estos recipientes las raíces crecen rápidamente lo que redunda en varios de los beneficios buscados: Se reduce la mano de obra y se respeta el medio ambiente. Los recipientes se degradan y se transforma en materia orgánica.
Existen muchas macetas biodegradables pero ninguna con sargazo, el cual se produce en altas cantidades. Se comprueba que el sargazo realmente funciona como fertilizante, algo que debería ser llevado a gran escala y considerado como una alternativa rápida y productiva en el mundo de la agricultura moderna.

(2017) Godínez A. B., Mecot D., Martínez R. Plásticos biodegradables: Derivados a favor del tratamiento de nuestro entorno vital. BACHILLERATO UNAM SI.
(2019) María Antonia Malajovich. Guías de actividades Biotecnología: enseñanza y divulgación. Bioplasticos. Extraído el 17 de octubre del 2019 desde: http://www.bteduc.bio.br
(2015)D oyle, E. and J. Franks.. Sargassum Fact Sheet. Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute.
(2018) Gómez M. Rodríguez C.M. G y Echeverría L. Arribazones de macroalgas marinas: un tesoro del mar. Octubre-diciembre, volumen 69 número 4 revista ciencia.
Dreckmann, K. M. y Sentíes, A. (2013), “Los arribazones de algas marinas en el Caribe mexicano: evento biológico natural o basura en las playas”, Biodiversitas, 107:7-11.
(201) Lemaire, Francis. Cultivos en macetas y contenedores: Principios agronómicos y aplicaciones. Extraído el 19 de noviembre del 2019 desde: https://www.biotaxa.org/Phytotaxa/article/view/phytotaxa.387.3.3
Carrillo Dominguez, S.; Castro, María Isabel; Pérez Gil, Fernando Composicion quimica de mucrocystis pyrifera (sargazo gigante) recolectada en Verano e Invierno y su posible empleo en alimentación animal Ciencias Marinas, vol. 20, núm. 1, 1994, pp. 33-40 Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Ensenada, México. Extraído el 25 de octubre desde: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=48020103
NAVIA D. P., VILLADA H.S. Biotecnología en el Sector Agropecuario y Agroindustrial Vol 11 No. 2 (173-180) Julio – Diciembre 2013. IMPACTO DE LA INVESTIGACIÓN EN EMPAQUES BIODEGRADABLES EN CIENCIA, TECNOLOGÍA E INNOVACIÓN.
Regularly when people want to expand or redecorate their garden, they face the problem of transplanting the shoots from the pot to the soil where they want to grow. This resulting situation is complicated for two reasons, first many experts indicate that the transplant can be harmful to the crop, since it can mistreat and break its roots which either do not grow again once in the ground and the second, the current economic pots high economic and environmental costs. The project seeks to manufacture pots from sargassum, necessarily to different types of crops (horticulture, nurseries of ornamental plants, seasonal, forest, etc.), without affecting them and the land in which they are going to be planted for their increase. These pots are practical, useful and degradable. Avoid the shock that transplantation produces because this can be done without removing the plants from the substrate, it is not difficult that it degrades in a short time that benefits the plant, provides nutrients that the plants need to survive; and the roots will have no problem to continue growing after going through the walls of the pot, to reach the ground.
Alternatives to use sargassum should be sought since its massive arrival is causing environmental problems, on the other hand, people face the problem of the transfer of shoots or trees from the pot to the ground since transplanting can be harmful to plants, On the other hand, many find it difficult to cut the pot without destroying the roots. The root-impervious pots cause deformations in the roots and the plastic pots that proliferate lately as well as the plastic bag for cultivation turn out to be a serious problem of contamination for the environment.
Pelagic sargassum is a brown algae, or algae that floats freely in the ocean and never sticks to the ocean floor, providing refuge for migratory species and essential habitat for more than 120 species of fish and more than 120 species of invertebrates. Sargassum is constantly circulating between the Sargasso Sea (in the Atlantic Ocean), the Caribbean, the Gulf of Mexico and the Gulf Stream.

Being a floating organism, sargassum moves through the ocean carried by wind and ocean currents and occasionally naturally reaches the coast. However, since 2011 a massive and sustained growth of these species has been observed in the Atlantic, reaching a length of 8,850 kilometers in 2018 (approximately the distance that exists between CDMX and Patagonia), forming what has been called the “Great Sargassum Belt” with a biomass of approximately 20 million tons; a figure equivalent to 10 times the total national annual fishing and mariculture.


The origin of this unprecedented phenomenon is linked to changes in the winds and hydrodynamics of the currents caused by climate change that could be bringing sargassum from the east (Africa) carried by zonal currents, or coming from the southern coast. American continent (Brazil), or come from the Sargasso Sea.

Increase in the discharges of organic matter and nutrients (Amazon River) that favors the growth of Sargassum algae, which double their growth rate in less than 18 days. Increase in the surface temperature of the oceans that favors the detachment of sargassum from its substrate.

It has had a very significant negative impact because if the sargassum continues to arrive in the volume registered in 2015 and 2018 and it is not given adequate management, the tourism industry of Quintana Roo may collapse causing economic losses due to cancellations, loss of jobs due to the decrease tourism, impact on the local economy (community service providers), in addition to the increase in beach management and cleaning costs in hotels.
The negative aspect of the landscape in the beaches and coastal area in general, causes losses in tourism. Increased costs for beach cleaning.
The volume of sargassum that arrived during 2019 exceeded the hotels ability to remove it.
Sargassum has been shown to produce reduced light and oxygen (hypoxia and anoxia), increased concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus (eutrophication), contamination of the soil and the ocean by the generation of sulfhydric acid (H2S) and ammonia (NH3 ), in addition to the bad smell that this causes.
The ecological reserves of Sian Khan, Puerto Morelos, Akumal, are being affected, the mortality of coral reefs, Interference with the nesting and hatching of turtles, Mortality of seagrass near the coast, Mortality of various marine animals, Impact in fauna species associated with sargassum during removal.
Activities at sea Massive accumulation on the beach (with some dead animals), loss of beach as a consequence of the disappearance of seagrass meadows and by land removal activities.
Disruption of fishing activities on the coast and in the communities.
Economic losses of fishermen due to the death of fishing resources.
Boatmen upset because their machinery (boats) get stuck and damaged with sargassum.
Poor disposition of sargassum collected on beaches can contaminate the aquifer and affect the availability of water to coastal communities and contaminate the sea.
The decomposition of sargassum can cause health damage by breathing in the gases from sargassum derived from its accumulation (H2S and NH3).
It generates conditions for the breeding of flies as vectors of diseases for humans.
Health problems occur in bathers and aquatic service providers due to contact with sargassum (and the accompanying fauna).

Iodine Fucoxanthin – pigment with antioxidant activity.
Phenolic compounds – antioxidant activity Alginic acid and Fucoidan – hepatoprotective polysaccharides.
Anticoagulant, antiviral, antibacterial, antithrombotic, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, prebiotic, protect the gastric mucosa against the proteolytic activity of gastric juices, prevent infection in the stomach by Helicobacter.
Various studies and tests have been carried out to take advantage of sargassum, which have had excellent results; it has been used for animal feed, they build a house with sargassum bricks the portomorelense invention would be used in houses for low-income people in quintana roo and would help to face the problem of the massive collection of algae, materials for finishes, such as bricks and boards similar to wood, which can be a decorative option for the home, A company designed by a group of young Mexicans was founded in Cancun Quintana Roo, creating the first pilot plant to process sargassum in Mexico and obtain sodium alginate; Researchers have been able to obtain cellulose that could be used in more than 20 types of industries, sargassum as a substrate for fungi and sargassum bioplastic are the uses that have been given to this algae
. The following uses have been proposed:
• Biofertilizer
• Pest exterminator
• Positive effects on vegetable crops
• Plant growth activator
• Stimulates germination
• Corrector of acidity and mineral deficiency
• Snacks
• Biodegradable disposable material (disposable plates)
• Solid waste treatment plant, which transforms sargassum from a solid to a gaseous state in order to generate biogas, charcoal or electricity, without generating waste.
• Obtaining Biofuel (biogas and bioalcohol) and the resulting residue for compost or livestock feed.
In the transplant, air contact occurs, this stops its growth and stimulates the formation of secondary roots that occupy the entire volume of the pot.
The space of the pot is very small so the roots cannot extend to look for water and nutrients, so more attention needs to be paid to both irrigation and fertilization. And many of the potting substrates, in general, are poor in fertilizing elements and the excess water from the irrigation that comes out of the drainage hole is carrying nutrients, gradually impoverishing it. Biodegradable plastic pots do not help the environment at all, because they take a long time to decompose.
On the other hand, zargazo contains minerals that accelerate the growth of plants and is 100% biodegradable, since the use of plastics is currently being banned, this is an excellent option both at home and at the producer level.
According to the materials used, the number of variants in biodegradable pots can be classified into two main groups:
a) pots made of vegetable fibers and
b) flower pots made of processed materials.
The materials used in the pots made with vegetable fibers are paper, wood fiber, coconut fiber, jute, peat and Miscanthus. Some of these types have been around for several years for special applications. Nurseries have had very good experiences using paper pots to present ground cover plants for important clients in the service sector.
Fossil, renewable materials, or mixtures of both constitute the basis of biodegradable materials, these materials must be made mostly of renewable materials of plant origin.
In particular, the most commonly used materials to make biodegradable pots are peat, wood chips, coconut fiber, and recycled paper. With fibrous materials, plant growth is often better during cultivation, and soil colonization by roots after planting is faster.
There are different types of biodegradable pots on the market, mainly made with cardboard and natural fibers, but with water and moisture this material rots and tends to be an excellent nest for fungi, which can be detrimental to the health of the roots of the plants.
When people want to expand or redecorate their garden with new plantings, they face the uncomfortable problem of transferring shoots or trees from the pot to the ground. This situation is a complication for two reasons: first, many experts indicate that transplanting can be harmful to plants, and on the other hand, many find it difficult to cut the pot without destroying the roots.
In summary, in this action the roots of the plant are in danger and for those who love their gardens or make this work a job, it is a necessity to find a safer alternative. It is here that biodegradable pots are presented as the ecological solution to a need with a significant demand.
These pots are practical and useful for plants. They serve to avoid the shock of transplanting because you can transplant without removing the plant from the substrate, the pots are biodegradable and the roots can cross them without problems. This difference is very noticeable, especially in difficult conditions (cold, drought, unfavorable seasons …). Finally, the non-deformation of the root system ensures a good and fast fixation of the plant and a better exploration of the soil.
In Mexico there is already a company that joined this ecological trend: Sedano, a nursery located in Guadalajara, through the line called Ecopot. Its line of pots, consists of biodegradable pots perfect for home and garden, which can be used for growing plants, and later can be broken to allow the growth of roots and planted directly in the ground or used indoors with the flowers.
Ecopot pots are made from bamboo fiber, rice husk and straw, using a high pressure method combined with high temperatures. All the pots in this line do not contain wood or oil, are biodegradable and do not harm the environment.
Some companies make pots with long Kenaf fiber and they are the size necessary to accommodate the adequate volume of soil and the composition of the amendment that gives better results with each species to be used.
Maple Vila, a company from Uruguay that offers the market biodegradable pots for nurseries, made of cellulose and vegetable fiber.
Ecoforms, a company from California, USA offers are made from grain shells and natural agents. At no stage of the production process are pollutants used or produced.
CocoPot, a German company, makes biodegradable coconut and curly fiber pots, which are formed exclusively from compressed natural latex (rubber tree milk), a binder to form an elastic unit and nature supplies the raw materials in large quantities.
Alecoconsult International, company with presence in Africa, America, Asia and Europe pots made from plant-based fibers. The biodegradation process begins depending on the ambient temperature, relative humidity and microbial presence from the moment of application. Complete biodegradation depends on the thickness of the plastic.
Keep in mind that conventional polyethylene-based plastic pots do not biodegrade and generate a high level of residuality.
Importance of organic fertilizers The need to reduce dependence on artificial chemicals in different crops is forcing the search for reliable and sustainable alternatives. In organic agriculture, great importance is given to these types of fertilizers and they are increasingly being used in intensive crops.
We cannot forget the importance of improving some physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the soil and, in this sense, this type of fertilizers plays a fundamental role.
With these fertilizers, we increase the capacity of the soil to provide plants with the different nutrients they need.
Nutrient deficiencies sometimes occur. It consists of missing one or more of the 12 essential elements for any plant (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Magnesium, Calcium, Sulfur, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Zinc, Copper and Boron), which causes various symptoms.
Sargassum contains:
Calcium, phosphorous, sodium, potassium, iron, manganese, copper and zinc in the essential amounts that feed plants and help them grow better.
Prepare pots based on sargassum since it is rich in nitrogen, which is a primary element of plants, to favor them as a fertilizer and which can serve as a substrate providing essential minerals.
We are interested in this topic because massive amounts of sargassum are arriving on the beaches of the Caribbean, due to the increase in the discharges of organic matter and nutrients that favor its growth (it is as if the sea told you I will return all the garbage that you have given me) , It is also affecting global warming since the increase in the surface temperature of the oceans which favors the detachment of sargassum from its substrate, finally the change in marine currents drags the sargassum to the beaches.
If we manage to make sargassum-based pots, then we would use a product that is rare, since it has properties that can be favorable to the development of the plant as well as being an economic and environmentally friendly product.

Water
Vinegar
Cornstarch
Dried sargassum
Oil
Measuring cup
Measuring spoons
Vegetable paint
Addressees Glasses to mold the pots
Sargassum should be collected offshore to ensure that it is alive and not in a process of decomposition.

Once collected, it is washed and left to dry perfectly in the sun.

Dried in the sun and crushed

Once you have the dried and crushed sargassum it is ready to use.

Put the corn starch in a bowl together with the water and the revolver until there are no lumps.

Put the gelatin in 200 ml to hydrate it

Simmer until the mixture changes color.

Put the vegetable coloring to give color to the pot.

Put the sargassum in abundant quantity, turn off the fire, put the vinegar and start kneading.

Put the dough in molds to shape it and let it dry for a few days.


Before starting the sprouting, water permeability and mechanical resistance tests were carried out.
Fill the pot with water and measure the time it takes to get through the walls. It is observed how the pot moistens and empties very quickly. (That is why the containers do not have holes in the base). Porosity is visible to the naked eye.


Force was applied to deform the container, failing to deform or break it.


Sargassum was placed in the small pots as a substrate for its sprouts and for serrano and habanero chile seeds.

Conventional garden soil and sargassum were used in the largest pots, seeds of serrano pepper, jalapeño were sown.

Commercial biodegradable pots were used to compare results.
They should be watered to keep the container moist, but without excess. Put them in a place with light, but not in direct sunlight.
It took 3 days to germinate in the sargassum pots.
Here the growth of the seeds is observed in a week. You can see that the first leaves have already come out.

The germination rate is very different between the pots, it is observed that in the sargassum pots they grew faster and more seeds germinated than in commercial biodegradable pots and the plastic one only germinated one seed more slowly than in the previous pots.
Its resistance is useful throughout the crop cycle, it does not break during transport and offers the plant a stable container.
We left two weeks like this, when the small plants have their long stems they are moved to the ground since the sargassum pots began to degrade and thus the growth of the roots was not slowed down by contact with air.
This helps the plant to improve the absorption of water and nutrients. Porosity forces more natural branching in the root structure.
A glass container was made to appreciate the degradation of the pots.

After 15 days to three weeks after the pots were put into the ground, the following results were obtained:

The pots degraded more quickly than the commercial biodegradable pots and in the plastic pot, it is observed that the plants in these pots have grown faster than the others.
The permeability, porosity and resistance of the pots are considered adequate.
Using the sargassum pot as fertilizer 15 days after transplant, it was observed that with the sargassum treatment, the plants grew better than those that did not have any treatment.

Comparing with plants planted in commercial biodegradable pots, better root development is observed in the biodegradable sargassum pot.

According to the literature, the rate of degradation is a function of different parameters related essentially to the microbial life of the soil, this suggests that in a short time and with a temperate climate, only small pieces of wall should remain after a few months.

The growth of these plants will continue to be monitored.


It is possible to manufacture biodegradable pots based on sargassum that turn out to be a low-cost product and suitable for different types of crops. The germinated plant in the biodegradable sargassum pot does not require a transplant: “pot in pot” or “pot in soil” can be introduced, without damaging the roots, allowing to advance the transplanting cycles in propagation and avoid transplant shock .
These containers are considered as an alternative for those who love their gardens or make this a job and look for “ready-to-plant” products. This is where biodegradable containers are presented as the ecological solution that meets a need in a safer and more secure way. an important demand.
When growing in these containers, the roots grow quickly, which results in several of the benefits sought: Reduced labor and respect for the environment. Containers degrade and transform into organic matter.
There are many biodegradable pots but none with sargassum, which is produced in high quantities. Sargassum is proven to really work as a fertilizer, something that should be taken on a large scale and considered a quick and productive alternative in the world of modern agriculture.

(2017) Godínez A. B., Mecot D., Martínez R. Biodegradable plastics: Derived in favor of the treatment of our vital environment. UNAM SI HIGH SCHOOL.
(2019) María Antonia Malajovich. Biotechnology activity guides: teaching and dissemination. Bioplastics. Extracted on October 17, 2019 from: http://www.bteduc.bio.br
(2015) D oyle, E. and J. Franks .. Sargassum Fact Sheet. Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute. (2018) Gómez M. Rodríguez C.M. G and Echeverría L. Arribazones of marine macroalgae: a treasure of the sea. October-December, volume 69 number 4 science magazine. Dreckmann, K. M. and Sentíes, A.
(2013), “The seaweed finches in the Mexican Caribbean: natural biological event or trash on the beaches”, Biodiversitas, 107: 7-11.
(201) Lemaire, Francis. Pot and container crops: agronomic principles and applications. Extracted on November 19, 2019 from: https://www.biotaxa.org/Phytotaxa/article/view/phytotaxa.387.3.3
Carrillo Dominguez, S .; Castro, María Isabel; Pérez Gil, Fernando Chemical composition of mucrocystis pyrifera (giant sargassum) collected in Summer and Winter and its possible use in animal feed Ciencias Marinas, vol. 20, no. 1, 1994, pp. 33-40 Autonomous University of Baja California Ensenada, Mexico. Excerpted on October 25 from: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=48020103
NAVIA D. P., VILLADA H.S. Biotechnology in the Agricultural and Agroindustrial Sector Vol 11 No. 2 (173-180) July – December 2013. IMPACT OF RESEARCH ON BIODEGRADABLE PACKAGING IN SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION.